👉Explain hello world program in java
This program has two main parts:
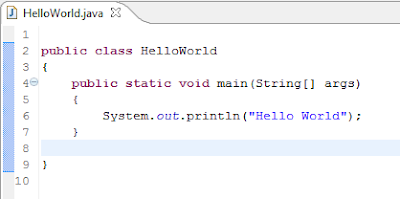
■ All the program is enclosed in a class definition—here, a class called HelloWorld.
■ The body of the program (here, just the one line) is contained in a routine called
main(). In Java applications, as in a C or C++ program, main() is the first
routine that is run when the program is executed.
You’ll learn more about both these parts of a Java application as the book progresses.
Once you finish typing the program, save the file. Conventionally, Java source files are named
the same name as the class they define, with an extension of .java. This file should therefore be
called HelloWorld.java.
Now, let’s compile the source file using the Java compiler. In Sun’s JDK, the Java compiler is
called javac.
To compile your Java program, Make sure the javac program is in your execution path and type
javac followed by the name of your source file:
javac HelloWorld.java
Note: In these examples, and in all the examples throughout this book, we’ll be
using Sun’s Java compiler, part of the JDK. If you have a third-party development
environment, check with the documentation for that program to see how to
compile your Java programs.
The compiler should compile the file without any errors. If you get errors, go back and make
sure that you’ve typed the program exactly as it appears in Listing 1.1.
When the program compiles without errors, you end up with a file called HelloWorld.class, in
the same directory as your source file. This is your Java bytecode file. You can then run that
bytecode file using the Java interpreter. In the JDK, the Java interpreter is called simply java.
Make sure the java program is in your path and type java followed by the name of the file without
the .class extension:
java HelloWorld
👉See More Videos About Java Programming Click Here
👉(// What the meaning of each
part (public, static, void, main, String and args): public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("This is my
first code. Awesome!"); } } // public: Mean that main () can be call from
anywhere // static: Mean that main () does not belong to a specific object //
void: Mean that main () returns no value // main: is the name of a function.
Main is special because is it start of a program // String: mean the data type
// args: args is the argument passed to the function. "args" is not
special and you can name it to anything else and the program would work the
same)

Post a Comment